WELCOME TO SUPRATHEL U
Welcome to the SUPRATHEL U training platform – created by experts for experts. Have fun exploring the product SUPRATHEL®, its use and application. Please feel free to contact our experts by phone or email with any questions.
SUPRATHEL® is a Class III medical device distributed in 36 countries across five continents. To date, more than 20,000 patients have been successfully treated in over 300 burn centers. SUPRATHEL® is based on polylactic acid and as an elastic membrane it mimics the natural skin. While being permeable to oxygen and water vapor it provides a physical barrier for microorganisms.
SUPRATHEL® is indicated in superficial (2a°) and deep dermal/partial thickness (2b°) skin loss diseases, such as burn wounds, split-thickness skin graft (STSG) donor sites, as well as trauma and surgical wounds. To learn more about the product please go to her www.suprathel.com or contact our experts.
Benefits of using SUPRATHEL®
Several advantages support the use and application of SUPRATHEL®
Significant pain relief1-3 – by up to 60%
Significantly less IV narcotic management required
Minimally manipulative dressing changes without anesthesia
Low rate of infections, no biologic risk3-5
Synthetic, biocompatible, absorbable
No reported allergic reactions, only few cases with infections and inflammation
Fast wound healing1,6,7,10
Improved early epithelization
Early mobilization can begin 2-5 days following application
Lower treatment costs2,4,5 – by up to 69%
One-time wound dressing, no change of SUPRATHEL® needed
Less care and aftercare needed, shortened need for hospitalization
Less administration of pain medication needed
Good cosmetic and functional outcomes and scar quality8,9
Reduced inflammatory reaction11
Literature
1 Uhlig et al. 2007: Burns. 33(2):221-9.
2 Schwarze et al. 2007: Burns. 33(7):850-4.
3 Schwarze et al. 2008: Ann Plast Surg. 60(2):181-5.
4 Everett et al. 2015: J Wound Care. 24(7):S4-8.
5 Glat et al. 2014: Abstract, 46th Annual Meeting of the ABA.
6 Lindford et al. 2011: Burns. 37(7):e67-72.
7 O´Brian et al. 2015: Abstract, 47th Annual Meeting of the ABA.
8 Kaartinen and Kuokkanen 2011: J Plast Surg Hand Surg. 45(4-5):200-3.
9 Keck et al. 2012: Burns.38(3):388-95.
10 Gürünlüoglu et al. 2019: J Burn Care Res, Jun 21;40(4):444-450.
11 Demircan et al. 2021: Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg Actions. Jan;27(1):122-131.
SUPRATHEL® is indicated for superficial and deep dermal/partial thickness 2nd degree skin loss diseases, areas (see white line in the burn classification for SUPRATHEL® indications).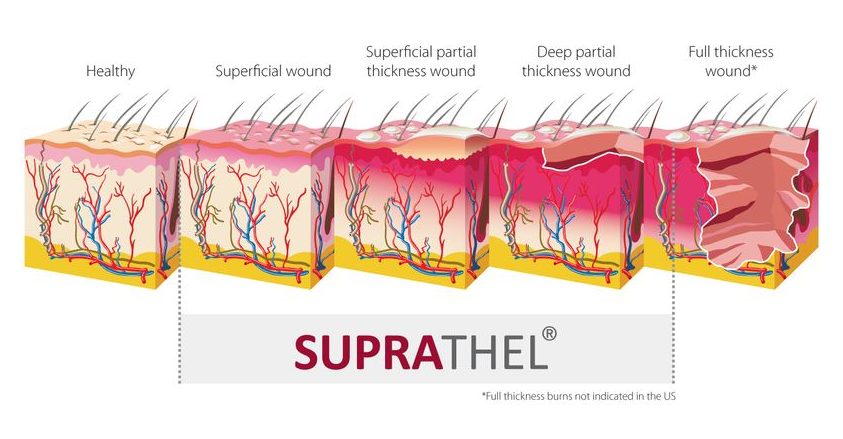
Second Degree Burns
Superficial Partial Thickness Burn (degree 2a)

2a degree burn with formation of blister on a child’s foot
- Blisters can be present
- Involvement of the entire epidermis and upperlayers of the dermis layers of the dermis
- Wound color will be pink or red
- Painful and appears wet
- Wound will blanch when pressure is applied
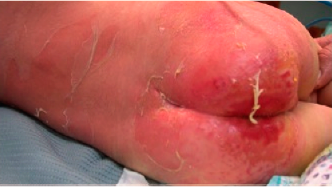
Second Degree Burns
Deep Partial Thickness Burn (degree 2b)

Mixed burns of degree 2a and 2b, right hand after an electric burn injury 1 day after debridement
- Wound may be red or white in color, appears dry
- Blister formation may occur
- Destruction of the entire epidermis and part of the dermis
- Blanching is sluggish or absent
- Sensation may be present, but diminished
Case Study 1 (PDF)
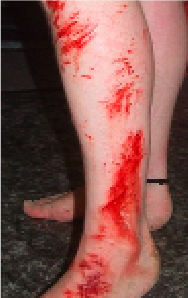
Split Skin Graft Donor Site

Extensive Skin Abrasion
Burn-like syndromes
In particular, SUPRATHEL® has been successfully used in so called “burn-like syndromes.” This describes the wide range of diseases manifested by extensive epidermal blistering and sloughing, as well as cutaneous necrosis requiring hospitalization and special intensive care management. Case Study 3 (PDF) TEN (Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis) (PDF)
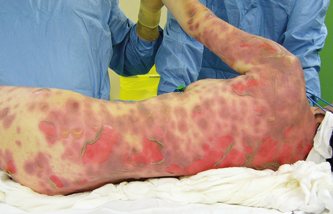
Skin lesions degree 2a, 80% BSA
5.1. Wounds caused by TEN (toxic epidermal necrolysis)
TEN (toxic epidermal necrolysis) is diagnosed in patients with an extensive loss of epidermis due to necrosis and a scalded-like appearance of the skin. TEN is the most serious drug-related skin eruption with a mortality rate between 11 and 70%. Patients with less than 10% of epidermal detachment are classified as having Stevens-Johnson Syndrome, while those with more than 30% of TBSA involvement are classified as having TEN.
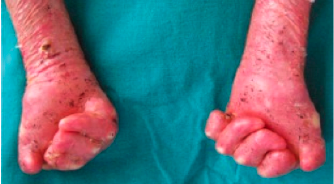
Dystrophic EB with flexion contractures of all fingers, adduction contracture of thumb, pseudosyndactyly, mittenlike deformity and blisters
5.2. EB (Epidermolysis bullosa)
EB (Epidermolysis bullosa) is a genetic defect and not a disease. There are a few case reports in which SUPRATHEL® was used. The primary advantage for this indication is faster wound healing.
SUPRATHEL® -assisted surgical treatment of the hand in epidermolysis bullosa patient (PDF)
Sheets of epidermal detachment on the patient’s back and diaper dermatitis as presented at the first admission to the operating room
5.3. SSSS (Staphylococcal Scalded Skin Syndrome)
SSSS is caused by infection with certain strains of staphylococcus bacteria resulting in skin damage with blisters, as if the skin were scalded.
An innovative local treatment for staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome (PDF)
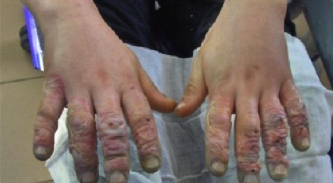
Clear blisters with haemoragic focal changes of eight fingers with associating edema
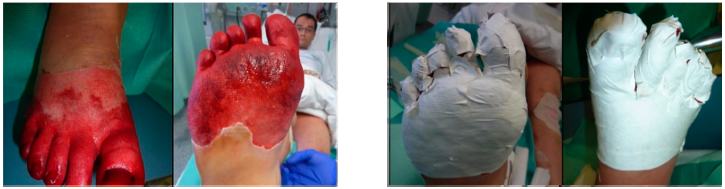
Application of SUPRATHEL on a forefoot’s frostbite. Courtesy of Dr. M. Rapp, Stuttgart
5.4. Frostbite
Frostbite is an injury caused by exposure of parts of the body due to freezing.
Lunchsymposium DAV 2011_Madry (PDF)
SUPRATHEL® used in combination with
6.1. Autologous grafts
SUPRATHEL® can also be ideally combined with autologous grafts, e.g. on top of expanded mesh grafts.

6.2. VAC® (Vacuum Assisted Closure)
SUPRATHEL® may also be applied together with VAC®
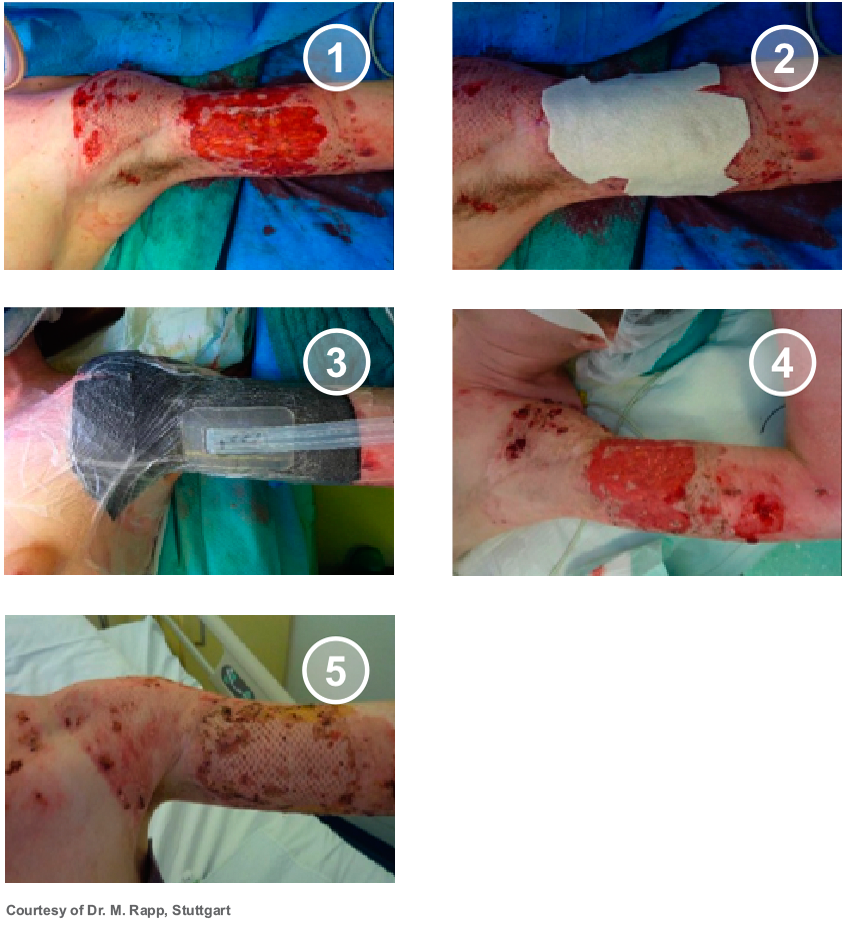
Body Areas
In general, SUPRATHEL® can be applied to any body area in children as well as in adults. Due to its plasticity, it can be moulded and is especially suitable for difficult-to-treat areas such as the face, neck, hands and joints. In case of a reduced or even missing availability of split skin grafts, SUPRATHEL® is ideal to bridge the time gap until availability meanwhile reducing the area that needs coverage by split-skin grafts. Large affected areas can thus be temporarily covered reducing the risk of infections while providing immediate pain relief.
As a basic rule, if the total body surface area (TBSA) is below 5% and pain management is the most important in the treatment plan, SUPRATHEL® should be the first choice.
In children, all body parts can be covered with SUPRATHEL®. Even if the deep dermis is partially affected, SUPRATHEL® functions as a temporary skin substitute and does not integrate into the skin.

- Infected wounds
- Exposed tendon / bone / cartilage / muscle
- Necrotic wound area
- Old burn wounds
- Heavily exuding wounds
- Tumors
How to avoid common mistakes
SUPRATHEL® may “swim off”
Insufficient debridement: consider surgical (sharp) debridement in deeper wounds. SUPRATHEL® applied too early after trauma: wait for 24 hours after trauma in case of deeper wounds. Consider Lavasept® / Hibiclens® dressing after debridement. Insufficient hemostasis: Use 1% adrenaline and warm towels. Consider light compression dressing during the first 1-3 days. Some users utilize stripes or staples around the edges to fixate SUPRATHEL®.
Double or even triple overlay of SUPRATHEL®
Overlap of membranes should be 2-5 inches (the fatty gauze must be clearly larger than SUPRATHEL®).
Too much tension when applying
Avoid stretching the membrane when applying.
Insufficient secondary dressing (fatty gauze)
1-2 layers of fatty gauze should do.
Removal too early or removal of fatty gauze
Be patient! Leave on wound. SUPRATHEL® – will peel off – after epithelialization. Just change outer dressing.
SUPRATHEL® gets wet before or during application
Change to dry gloves before application.
SUPRATHEL® gets hot before or during application
Avoid any heat sources (e.g. lamps) before application. The thin membrane gets warm quickly.
Outer dressing too thick (humidity cannot escape)
Avoid too thick outer dressing, so the wound can “breathe”.
What treatment is recommended for a contaminated wound?
At first, thorough disinfection and debridement. Then administer a local or systemic antibiotic. Local application of a disinfectant on SUPRATHEL® and monitoring of the inflammatory process secured by transparency of SUPRATHEL® and fatty gauze.
Can infections occur under SUPRATHEL®?
After thorough debridement, SUPRATHEL® forms a physical barrier against microorganisms. It also reduces the pH-value of the wound, thus inhibiting growth of bacteria and viruses.
In case of frequently which disinfectant can be used for debridement ?
Octenisept®
Lavasept®
Betadine® (colouring!)
Lavanid®Acetic acid 3%
Polyhexanide
Which fatty gauzes are recommended to apply on top of SUPRATHEL®?
Paraffinated gauzes such as
Vaseline® gauze
Bridal Veil or N-Terface® (in combination with Bacitracin®/Polysporin®)
Adaptic®
Bactigras®
Cuticerin®
Grassolind®
Jelonet® (most commonly used)
What if SUPRATHEL® dislocates?
Consider Lavasept® dressing after debridement.
Insufficient hemostasis: Use 1% adrenaline and warm towels.
Consider light compression dressing during the first 1-3 days.
Some users utilize stripes or staples around the edges to fixate SUPRATHEL®.
What are the storage temperatures?
SUPRATHEL® should be stored in a refrigerator between 8°C (46°F) and 22°C (71°F)
SUPRATHEL® is delivered in a cooling box keeping the temperature within this range. When the membrane is white and non-transparent, it is in proper condition.
Baartmans MG, Dokter J, den Hollander JC, Kroon AA, Oranje AP. Use of Skin Substitute Dressings in the Treatment of Staphylococcal Scalded Skin Syndrome in Neonates and Young Infants. Neonatology. 2011;100(1):9-13.
Blome-Eberwein SA, Amani H, Lozano DD, Gogal C, Boorse D, Pagella P. Burns. A bio-degradable synthetic membrane to treat superficial and deep second degree burn wounds in adults and children – 4 year experience. Burns. 2020 Aug 29;S0305-4179(20)30507-6.
Demircan M, Gürünlüoğlu K, Gözükara Bağ HG , Koçbıyık A, Gül M, Üremiş N, Gül S, Gürünlüoğlu S, Türköz Y, Taşçı A. Impaction of the polylactic membrane or hydrofiber with silver dressings on the interleukin-6, tumor necrosis factor-α, transforming growth factor-b3 levels in the blood and tissues of pediatric patients with burns. Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg. 2021 Jan;27(1):122-131.
Everett M, Massand S, Davis W, Burkey B, Glat PM. Use of a copolymer dressing on superficial and partial-thickness burns in a paediatric population. J Wound Care. 2015 Jul;24(7):S4-8.
Fischer S, Kremer T, Horter J, Schaefer A, Ziegler B, Kneser U, Hirche C. Suprathel(®) for severe burns in the elderly: Case report and review of the literature. Burns. 2016 Aug;42(5):e86-92.
Gürünlüoğlu K, Demircan M, Taşçi A, Üremiş MM, Türköz Y, Bağ HG, Akinci A, Bayrakçi E. The effects of two different burn dressings on serum oxidative stress indicators in children with partial burn. J Burn Care Res, Jun 21;40(4):444-450.
Gürünlüoğlu K, Demircan M, Koç A, Koçbıyık A, Taşçı A, Durmuş K, Gürünlüoğlu S, Gözükara Bağ H. The Effects of Different Burn Dressings on Length of Telomere and Expression of Telomerase in Children With Thermal Burns. J Burn Care Res. 2019 Apr 26;40(3):302-311.
Harenberg PS, Hrabowski M, Ryssel H, Gazyakan E, Germann G, Engel H, Reichenberger MA. Febrile Ulceronecrotic Mucha-Habermann Disease. Eplasty. 2010 Jul 16;10: e53.
Highton L, Wallace C, Shah M. Use of Suprathel® for partial thickness burns in children. Burns. 2013 Feb;39(1):136-41.
Hundeshagen G, Collins VN, Wurzer P, Sherman W, Voigt CD, Cambiaso-Daniel J, Nunez Lopez O, Sheaffer J, Herndon DN, Finnerty CC, Branski LK. A Prospective, Randomized, Controlled Trial Comparing the Outpatient Treatment of Pediatric and Adult Partial-Thickness Burns with Suprathel or Mepilex Ag. J Burn Care Res. 2018 Feb 20;39(2):261-267.
Kaartinen IS; Kuokkanen HO. Suprathel(®) causes less bleeding and scarring than Mepilex(®) Transfer in the treatment of donor sites of split-thickness skin grafts. J Plast Surg Hand Surg. 2011 Sep;45(4-5):200-3.
Keck M, Selig HF, Lumenta DB, Kamolz LP, Mittlböck M, Frey M. The use of Suprathel(®) in deep dermal burns: First results of a prospective study. Burns. 2012 May;38(3):388-95.
Lindford AJ, Kaartinen IS, Virolainen S, Vuola J. Comparison of Suprathel® and allograft skin in the treatment of a severe case of toxic epidermal necrolysis. Burns. 2011 Nov;37(7):e67-72.
Liodaki E, Schopp BE, Lindert J, Krämer R, Kisch T, Mailänder P, Stang F. Kombination von universellem Antidot und temporärem Hautersatz bei Verätzungen [Combination of a universal antidote and temporary skin substitute for chemical burns: Extended case report]. Unfallchirurg. 2015 Sep;118(9):804-7.
Madry R; Struzyna J; Stachura-Kulach A; Drozdz L; Bugaj M. Effectiveness of Suprathel® application in partial thickness burns, frostbites and Lyell syndrome treatment. Pol Przegl Chir. 2011 Oct 1;83(10):541-8.
Markl P, Prantl L, Schreml S, Babilas P, Landthaler M, Schwarze H. Management of split-thickness donor sites with synthetic wound dressings: results of a comparative clinical study. Ann Plast Surg. 2010 Nov;65(5):490-6.
Merz KM, Sievers R, Reichert B. Suprathel® bei zweitgradig oberflächlichen Verbrennungen im Gesicht [Suprathel® for coverage of superficial dermal burns of the face]. GMS Verbrennungsmedizin 2011, Vol 4, ISSN 1869-1412.
Mueller E, Haim M, Petnehazy T, Acham-Roschitz B, Trop M. An innovative local treatment for staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2010 Jul;29(7):893-7.
Nolte SV, Xu W, Rodemann H-P, Rennekampff H-O. Suitability of Biomaterials for Cell Delivery in Vitro. Osteo trauma care 2007; 15(1):42-47.
Pfurtscheller K, Trop M. Phototoxic Plant burns: Report of a Case and Review of Topical Wound Treatment in Children. Pediatr Dermatol. 2014 Nov-Dec;31(6):e156-9.
Pfurtscheller K, Zobel G, Roedl S, Trop M. Use of Suprathel dressing in a young infant with TEN. Pediatr Dermatol. 2008 Sep-Oct;25(5):541-3.
Rapp, M, Uhlig C, Dittel K-K. The Treatment of Mass Burn Casualties Resulting from Mass Disaster. Osteo trauma care 2007; 15:8-16.
Rashaan ZM, Krijnen P, Allema JH, Vloemans AF, Schipper IB, Breederveld RS. Usability and effectiveness of Suprathel® in partial thickness burns in children. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2017 Aug;43(4):549-556.
Ring A, Tilkorn D, Ottomann C, Geomelas M, Steinstraesser L, Langer S, Goertz O. Intravital monitoring of microcirculatory and angiogenic response to lactocapromer terpolymer matrix in a wound model. Int Wound J. 2011 Apr;8(2):112-7.
Rothenberger J, Constantinescu MA, Held M, Aebersold DM, Stolz A, Tschumi C, Olariu R. Use of a Polylactide-based Copolymer as a Temporary Skin Substitute for a Patient With Moist Desquamation Due to Radiation. Wounds. 2016 Jul;28(7):E26-30.
Sari E, Erylmaz T, Tetik g, Ozakpinar HR, Eker E. Suprathel®-assisted surgical treatment of the hand in a dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa patient. Int Wound J. 2014 Oct;11(5):472-5.
Schiefer JL, Rahmanian-Schwarz A, Schaller HE, Manoli T. A Novel Hand-shaped Suprathel simplifies the Treatment of Partial-Thickness Burns. Adv Skin Wound Care. 2014 Nov;27(11):513-6.
Schwarze H, Küntscher M, Uhlig C, Hierlemann H, Prantl L, Noack N, Hartmann B. Suprathel, a new skin substitute, in the management of donor sites of split-thickness skin grafts: results of a clinical study. Burns. 2007 Nov;33(7):850-4.
Schwarze H, Küntscher M, Uhlig C, Hierlemann H, Prantl L, Ottomann C, Hartmann B. Suprathel, a new skin substitute, in the management of partial-thickness burn wounds: results of a clinical study. Ann Plast Surg. 2008 Feb;60(2):181-5.
Selig H, Keck M, Lumenta DB, Mittelböck M, Kanmolz LP. The use of a polylactide-based copolymer as a temporary skin substitute in deep dermal burns: 1-year follow-up redults of a prospective clinical noninferiority trial. Wound Repair Regen. 2013 May-Jun;21(3):402-9.
Uhlig C, Rapp M, Dittel KK. Neue Strategien zur Behandlung thermisch geschädigter Hände unter Berücksichtigung des Epithelersatzes Suprathel [New strategies for the treatment of thermally injured hands with regard to the epithelial substitute Suprathel]. Handchir Mikrochir Plast Chir. 2007 Oct;39(5):314-9.
Uhlig C, Rapp M, Hartmann B, Hierlemann H, Planck H, Dittel KK. Suprathel-an innovative, resorbable skin substitute for the treatment of burn victims. Burns. 2007 Mar;33(2):221-9.
Uhlig C, Hierlemann H, Dittel K-K. Actual Strategies in the Treatment of Severe Burns – Considering Modern Skin Substitutes. Osteo trauma care 2007; 15:2-7.
PolyMedics Innovations Inc.
645 Molly Lane, Suite 100
Woodstock, GA 30189
United States
Tel: +1 646 604 2771
Fax: +1 646 350 3129
Email: info.usa@polymedics.com
We appreciate your comments on the content of this new website. Let us know what we can do to meet your needs.
By sending your message you accept our data privacy policy.
